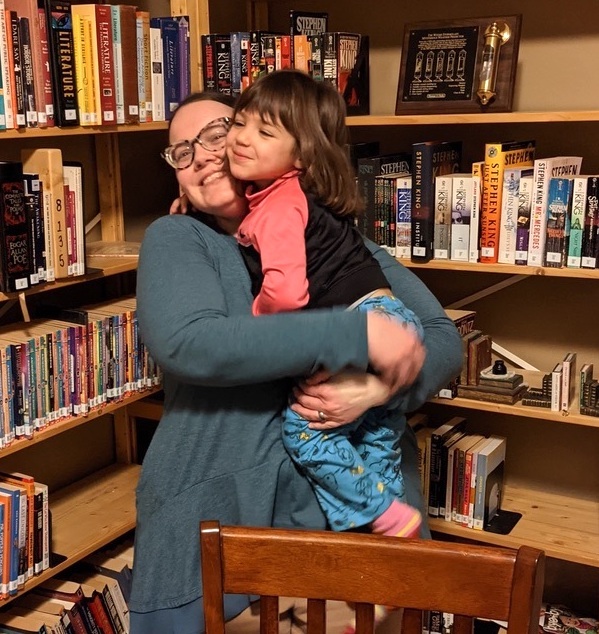
Martha Brockenbrough (Photo by Emerald England)
March 4th is National Grammar Day. Established by author Martha Brockenbrough, the day was designated as a holiday in 2008. To celebrate, Meg sat down (virtually) with Brockenbrough to talk about grammar in our world today.
Let’s start with the basics: how do you define grammar and why do you think it’s important?
Oh, this could be a very long answer. Let me start with something fun: grammar and grimoire share an ancestor. A grimoire is a magician’s manual for invoking demons and you could say that grammar can often be the same. What they have in common is magic. There is the good magic that helps us say what we mean to say and understand what is meant by the author. And then there is the bad magic that uses grammar to exclude, humiliate, and subjugate. Grammar is understanding how our language works, how it has evolved, and what can be accomplished by respecting conventions and what can be accomplished by breaking them. The more we know, the more powerfully and humanely we can practice this wonderful art.
You established National Grammar Day in 2008 with the goal of making grammar fun and lively for your students. How has grammar, or the study of grammar, changed in the last thirteen years?
I’m no longer teaching high school students, although I have one at home. I think for some, the study of grammar has changed in some of the good ways that society has changed. We are better now at recognizing white supremacy and the marginalization of certain forms of English. Language has always been a political weapon. English follows a lot of Latin “rules” for this exact reason. Latin was viewed as a superior language, and we were clawing our way upward in modeling certain English rules—e.g. “don’t split infinitives”—on Latin, where an infinitive is a single word and can’t be split.

In America, we just got rid of a president who was incredibly sloppy with language. When his subordinates tweeted under his name, they even copied his irregular spelling and capitalization. I’m being judgmental here. I called him sloppy. But as the parent of a child with dyslexia, I recognize that he might also have this very common learning disability. So my judgment might be unfair even as he played the role of a populist, and part of that role is rejecting the appearance of being conventionally educated. This was, I suppose, his evil genius. He could be born with a golden spoon in his mouth and convince people without his privilege that he understood them.
Part of arming ourselves against future demagogues is, I think, in not using education and knowledge as a cudgel to beat anyone down, but rather, to insist that it is both a gift and a birthright for everyone. I believe in building windows and doors, not walls. If it were easy, we would have done this long ago. And maybe I wouldn’t be so judgmental about the disgraced, twice-impeached, former president’s language. But I do think that’s what we might all work toward.
A lot of our members are at home helping their kids or grandkids with school because of the pandemic. What do you hope adults will convey to young people about grammar?
The best way to learn how language works is to read a lot. When you read, you encounter a much wider vocabulary than you do when conversing, watching TV, or listening to the radio. You also internalize patterns of language that have met a certain threshold of excellence. Everyone ought to read like crazy, and most libraries are still making this possible.
Meanwhile, I think we might do less conveying and more listening. I’m always learning new things about the evolving language from my kids. It was news to me that terminal punctuation on texts conveyed anger to them. To me, it meant I was being careful and consistent. All sorts of new vocabulary comes from young people, and it doesn’t hurt us to learn it and understand it. I do confess to taking delight in using things incorrectly, just to rile my kids a bit. But now it’s a running gag. They stan it. Or something like that.
I still do convey certain things to my daughters, who are now 17 and 20. The language we use in public—on social media and in school—is a lot like the clothes we wear. There are expectations and conventions. There are also power dynamics. A person who is hiring people for a job has power over the applicants, and that’s why we scrutinize our resumes and dress strategically for interviews. That’s a different situation from hanging out with friends (wearing masks, staying six feet apart). Navigating the world is easier when you understand conventions, dynamics, and codes, some of which probably ought to dismantled, but that can be hard to do from the outside.
In addition to being a grammar champion, you write fiction and narrative nonfiction. How does your understanding of grammar impact your creative writing?
I’m reading a most wonderful book right now: A Swim in the Pond in the Rain by George Saunders, which is a close examination of Russian short stories and how he teaches them. Here we are, reading translations of work, and translating them again through the eyes of Saunders, who is a white man of a certain age with certain experiences. Look at what language can do. Look at what stories can do. They can cross continents. They can travel through time. They can be funneled through the filter of another language twice—and still mean something to the reader. I’m paraphrasing, but one thing Saunders says is that he tries to write sentences that make the reader want to read the next one.
That is a very specific vision of how stories work. If you’ve ever studied storytelling, you no doubt know there are graphs that show us how stories work. That there are “beats.” Narrative structures. Big-picture things that suggest that the shape of the story is more important than its cellular structure.
What Saunders is talking about, I think, is partly the power of grammar. When you encounter a sentence that is right for the story—the right words in the right order with the right rhythm for the emotional moment—you want to know what happens next. This is a way of tying the big picture elements to the very smallest, the way our bodies emerge from our unique double helixes of DNA.
All of which is to say that when I am telling a story, I make the best use I can of every tool possible. Grammar—conventional, unconventional, character-specific—is vital.
Tell us about your home library.
I love books. I have many. Too many. It is badly organized, though it wasn’t always that way. It makes it hard to find specific things but easy to be surprised by treasure. It is a mix of books for young readers and books for grownups, mostly fiction for the former and nonfiction for the latter. On the project list this year are more built-in bookshelves, and we just secured some reclaimed fir for the purpose. I’m giddy with excitement.
Tell us what you’re reading right now.
I just finished David Sedaris’s essay collection, The Best of Me. I’ve been reading him my entire adult life. I’ve seen him live. I’ve read some of these essays before, and this collection felt a bit like a reckoning about family, what is funny, and what fractures us. I am reading A Question of Freedom by Reginald Dwayne Betts, which is his memoir about coming of age in prison. And then there’s the Saunders book. I don’t generally read so many books by men, but sometimes it happens. I just finished the page proofs of my next novel, Into the Bloodred Woods, which is based on the idea that everything you’ve ever read in fairytales is a lie.
About Martha Brockenbrough:
Martha Brockenbrough is the author of two books for adults and numerous books for young readers, including YA fiction and nonfiction, picture books, and a forthcoming chapter book series. Her next book, Into the Bloodred Woods, will be released by Scholastic in November. Visit her website to learn more about her and her books.
 Win free books from the May 2021 batch of Early Reviewer titles! We’ve got 94 books this month, and a grand total of 2811 copies to give out. Which books are you hoping to snag this month? Come tell us on Talk.
Win free books from the May 2021 batch of Early Reviewer titles! We’ve got 94 books this month, and a grand total of 2811 copies to give out. Which books are you hoping to snag this month? Come tell us on Talk.



 Publishers do things country-by-country. This month we have publishers who can send books to the US, Canada, the UK, Israel, Australia, France, Germany, and many more. Make sure to check the flags by each book to see if it can be sent to your country.
Publishers do things country-by-country. This month we have publishers who can send books to the US, Canada, the UK, Israel, Australia, France, Germany, and many more. Make sure to check the flags by each book to see if it can be sent to your country.















































































































































































































































































