This month’s State of the Thing, LibraryThing’s monthly newsletter of features, author interviews and various forms of bookish delight, should have made its way to your inbox by now. You can also read it online. It includes author interviews with Rebecca Stott and Dustin Thomason.
 I talked to Rebecca Stott about her latest book, Darwin’s Ghosts: The Secret History of Evolution, published by Spiegel & Grau. Some excerpts:
I talked to Rebecca Stott about her latest book, Darwin’s Ghosts: The Secret History of Evolution, published by Spiegel & Grau. Some excerpts:
Tell us about Darwin’s Ghosts—how did the idea for the book come about, and how did you select which subjects to profile?
When I wrote Darwin and the Barnacle back in 2003 I was struck once again by the dangerousness of the work Darwin was doing. I knew there had been others who had entertained ideas about the evolution of species before him and I became curious about the risks they might have undertaken. I started with Darwin’s own list of his predecessors—there were 38 men on Darwin’s list—and began to assemble as many more names as I could find. My book begins with Aristotle, even though Darwin was mistaken to call him an evolutionist, because the questions he was asking and the empirical methods he used would shape the long history of evolution in important ways. My aim was to try to understand these people as human beings not just as vehicles for ideas. I wanted to know what vexed them, what woke them up at night, what drove them.
What was it that persuaded Darwin to add his “Historical Sketch” to the third edition of Origin (and to expand it in the fourth edition)? Was there any contemporary reaction to the essay itself (distinct from reaction to the book as a whole)?
There was a kind of protocol in Darwin’s time that if you published a groundbreaking book of science you would begin by paying tribute to all the thinkers who had walked that path before you. Darwin failed to do this with Origin partly because he was rushed into print and partly because he was unsure just who his predecessors were. In 1860, when he was chastised for not including such a preface, he resolved to write one. The project took him six years to complete and was a source of enormous anxiety to him; he was never quite sure who had said or written what and when. Because he kept finding new people the historical sketch was always to some degree a work-in-progress.
You write in the preface about growing up in a household where the Darwin entry was literally razored out of the encyclopedia. Do you think that contributed to your interest in Darwin and his ideas?
Undoubtedly—as far as one can know about these things. I was a curious child, and I remember the intense frisson of curiosity I felt about Darwin and his ideas, because they were regarded with such derision and horror by all the important men in the religious community I lived in. Prohibition acts in mysterious ways.
Which of Darwin’s predecessors were you most surprised to learn about as you researched for this book?
Probably the eighteenth-century French intellectual Diderot. I lingered longer over that chapter than any of the others. I think I fell in love with him a little. Diderot was intellectually restless, a rule-breaker, a risk-taker, clearly also fascinating and charismatic in conversation. I think he might well be the most original thinker I have encountered. Because he was forced to hide his ideas—he was under surveillance from the Paris police—he developed a series of rhetorical strategies for evading responsibility often by using devices from the theatre. The results are often surreal and highly inventive.
Read the rest of our interview with Rebecca Stott.
 I had the chance to talk with Dustin Thomason about his new thriller 12.21, published by The Dial Press.
I had the chance to talk with Dustin Thomason about his new thriller 12.21, published by The Dial Press.
Do you recall what first made you think about combining prions and Mayan prophecies for the plot of 12.21?
That was actually what brought the entire book together for me and is one of the key secrets of the book! The connection is deeply rooted in the culture of the ancient Maya, and closely connected to the original way that prions were discovered. But to really find out, you’ll have to read on …
Your book features a fictional Mayan codex, but there are a few of these that actually exist. Tell us about the codices and their importance in our understanding of Mayan civilization and culture.
Four ancient Maya books still exist of the thousands of screen-folded codices that probably once filled the royal libraries. You can find images of several of them online and see the wondrous work of the ancient scribes that served as the jumping off point for the codex in 12.21. The scribes were meticulous bookkeepers, and in these codices they kept close records of rituals and astronomical matters, all dated according to the all-important cyclical calendars responsible for the 2012 phenomenon. Amazing naked-eye astronomers, many Maya books were almanacs that tracked the movement of Mars and Venus, solstices and equinox, as well constellations eerily similar to our own zodiac. Over the last century, Mayanists have been able to use these four remaining books—named the Dresden, Madrid, Paris and Grolier codices—to bring the most advanced civilization in the pre-Columbian new world back to life.
What’s your library like today? What sorts of books would we find on your shelves?
A very eclectic mix. On the fiction side, you’d see Stephen King and Michael Crichton and Richard Russo, plus Dan Brown and Dickens and Philip Roth and Delillo and Lehane and Michael Cunningham, to name a few. Many shelves I’m looking at now are taken up by books about the ancient Maya, some of them out of print. In order to write in the voice of a ninth century scribe, I had to immerse myself in most everything that’s been written about them. You’d also find dozens of medical textbooks, and a weird assortment of other things on random topics that most people would find absurd. As I glance higher, I see And the Band Played On sandwiched between The Professional Handbook of the Donkey and The White Album. Plus, for Christmas every year, my father used to give us The World Almanac, so there’s almost two entire shelves taken up by those alone.
Which books have you read recently that you enjoyed?
Michael Olson’s Strange Flesh recently enchanted me with its weird and wonderful mix of hacker noir and depraved hearts, and I just finished William Landay’s Defending Jacob, which sucks you in with its compelling voice from page one and takes you on a ride of twists and turns as good as any since Presumed Innocent. I also just went to the Middle East for the first time, and while I was there I read Exodus, which seemed as fresh now as it must have to readers fifty years ago.
Read the rest of our interview with Dustin Thomason.
Catch up on previous State of the Thing newsletters.
If you don’t get State of the Thing, you can add it in your email preferences. You also have to have an email address listed.







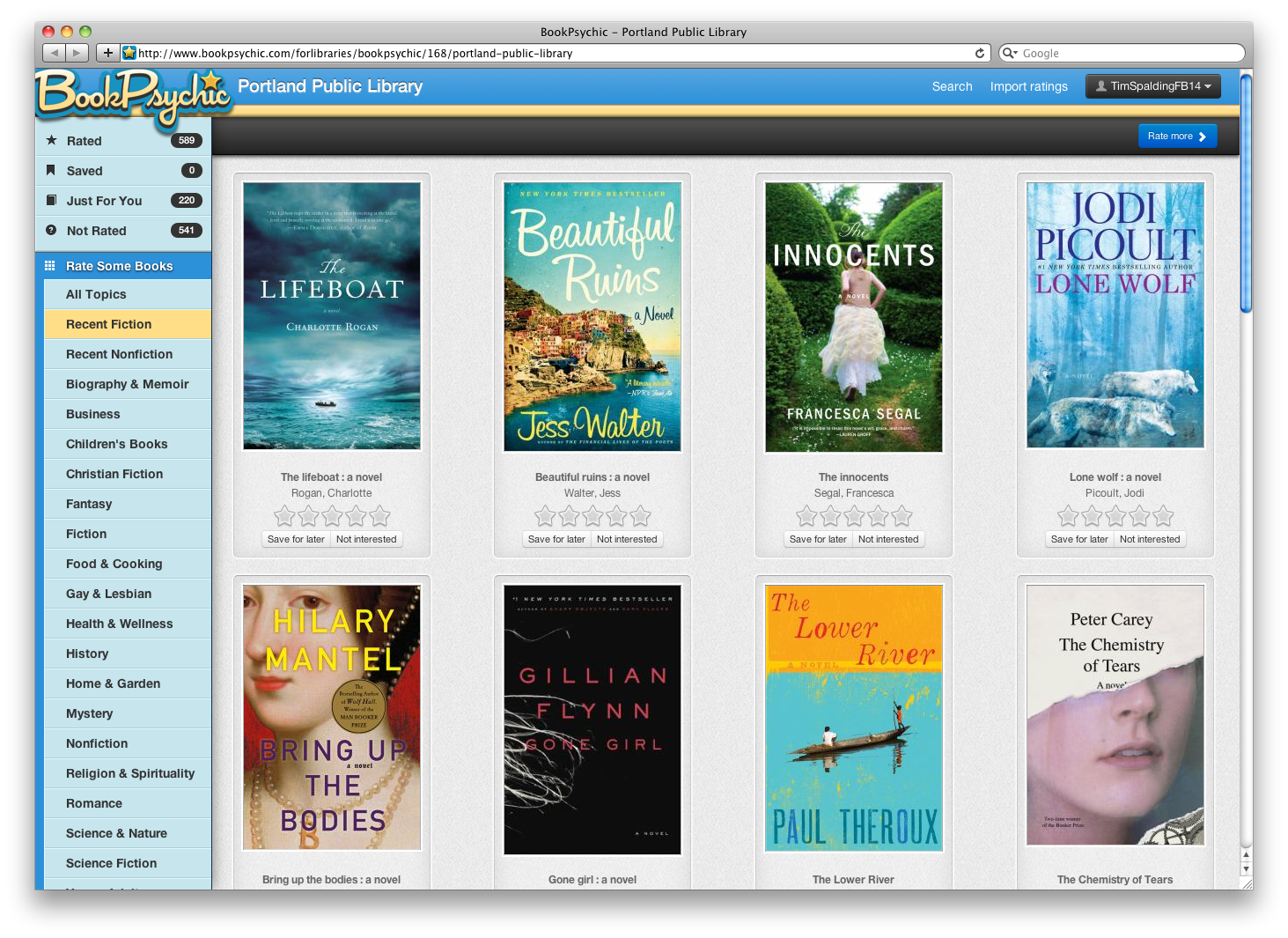









 Publishers do things country-by-country. This month we have publishers who can send books to the US, Canada, the UK, and more. Make sure to check the flags by each book to see if it can be sent to your country.
Publishers do things country-by-country. This month we have publishers who can send books to the US, Canada, the UK, and more. Make sure to check the flags by each book to see if it can be sent to your country.


































































































































